
Vision Network Analysis
Planning, design and control of transport, distribution and industrial grids.
Vision Cable Analysis enables you to easily calculate the load capacity of cables. The program uses the IEC 60287 (stationary load capacity) and IEC 60853 standard (dynamic load capacity), allowing it to calculate both 'simple' continuous as well as temporary and cyclical loads.

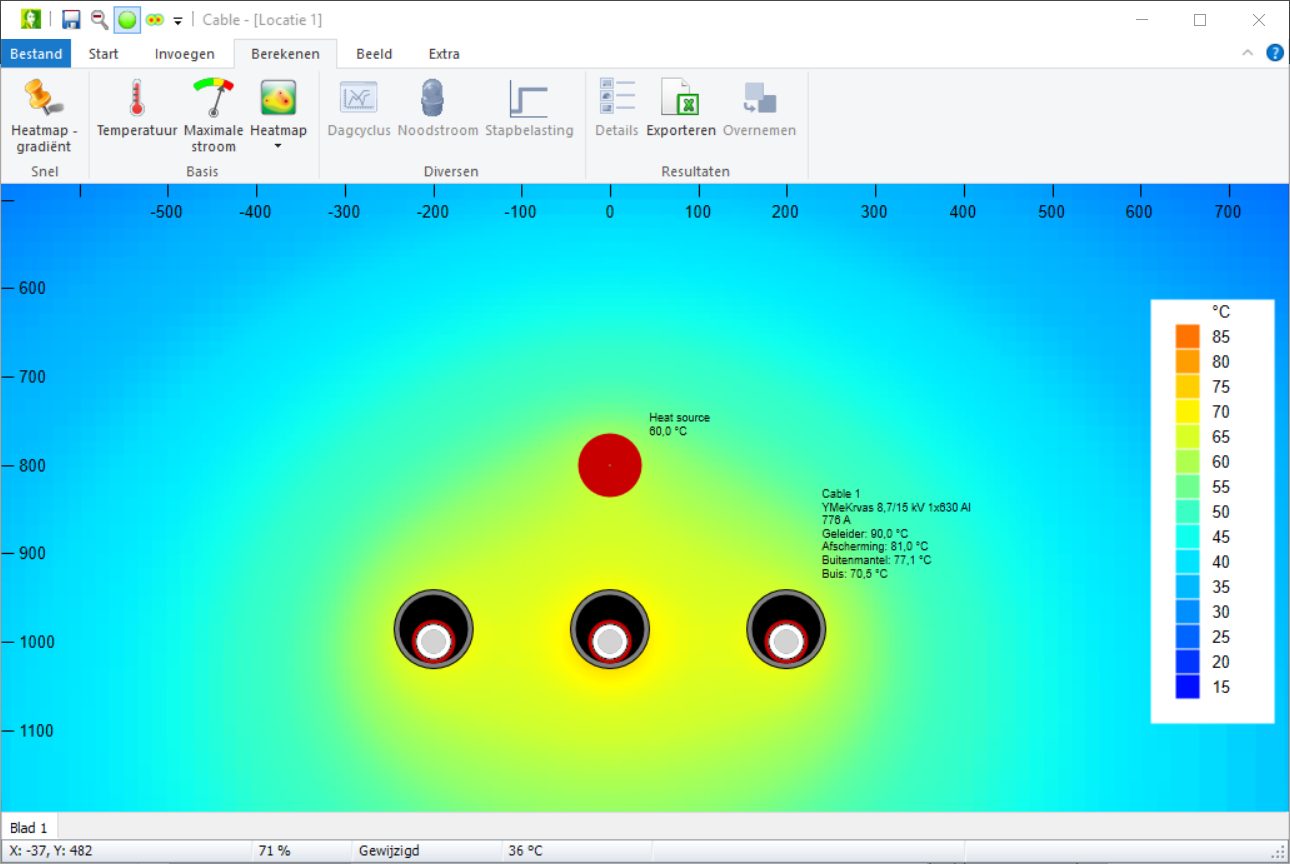
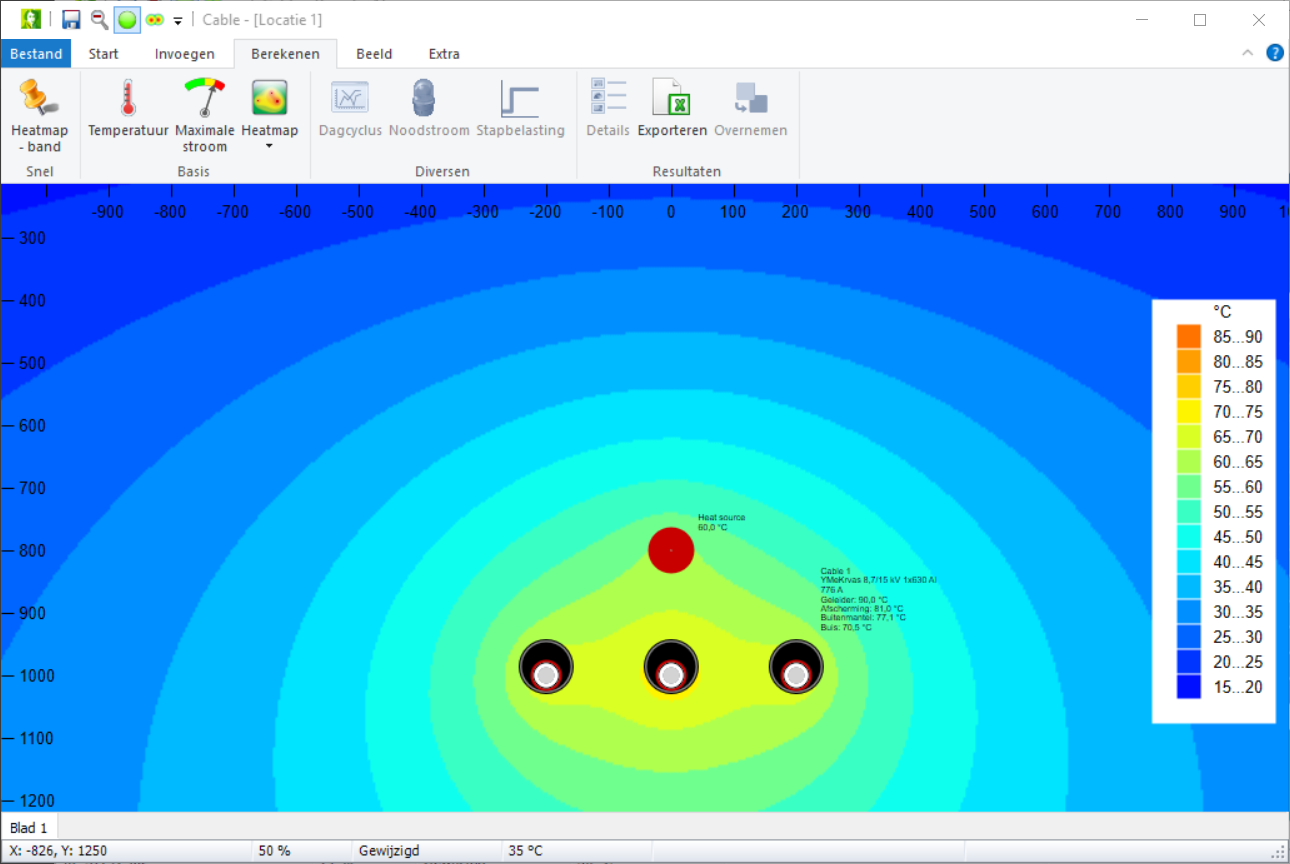
Vision Cable Analysis calculates the temperature of cables and their environment, taking into account the environment and possible external heat sources.
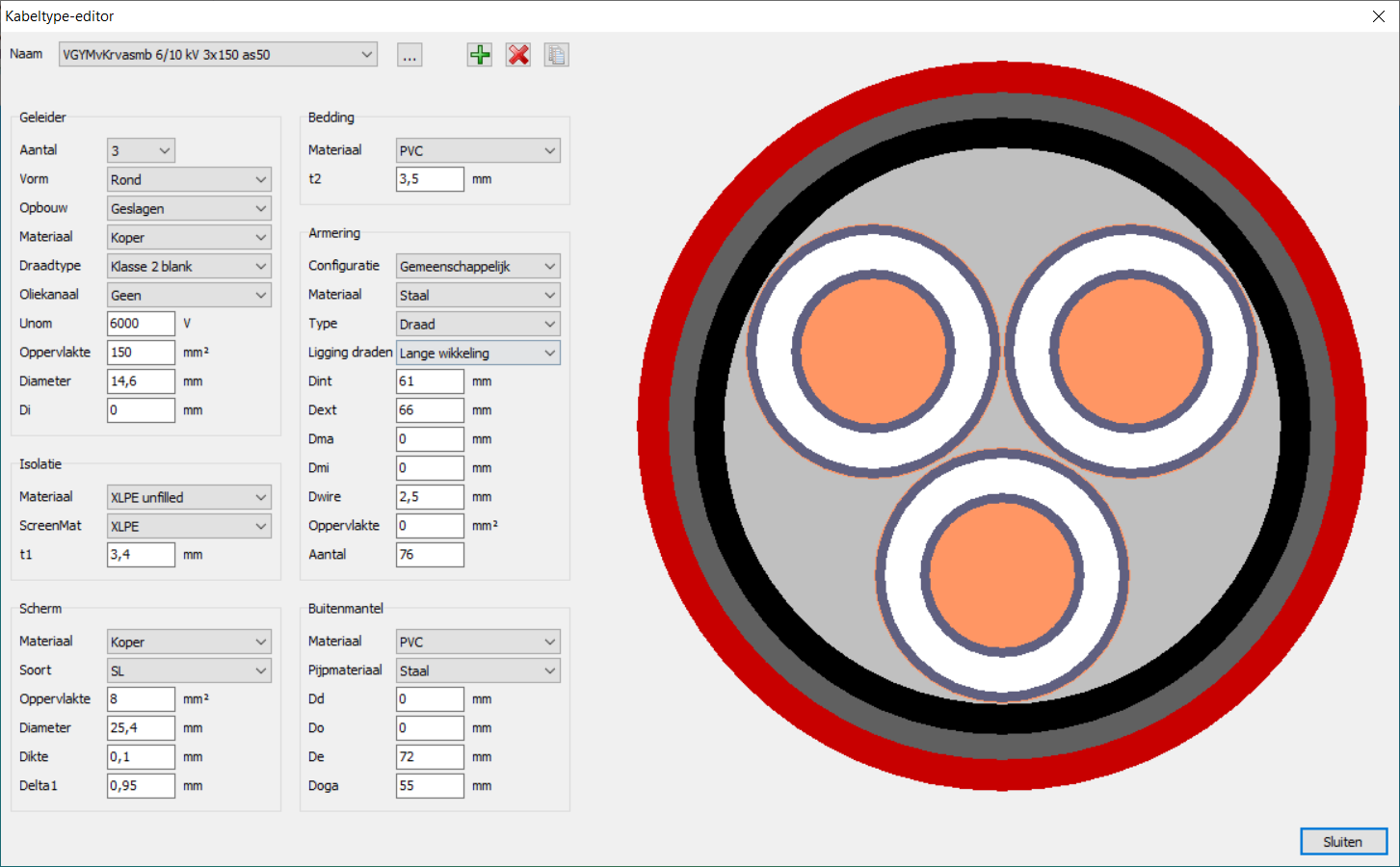
Vision Cable Analysis comes with an extensive database of the most commonly used cables. Users can easily modify cables and define additional cable models.
The IEC 60287 standard describes the methods for calculating cable losses and the thermal resistance of the cable and its environment.
Vision Cable Analysis calculates:
The results of the calculations are presented graphically, with any change or adjustment immediately visible.
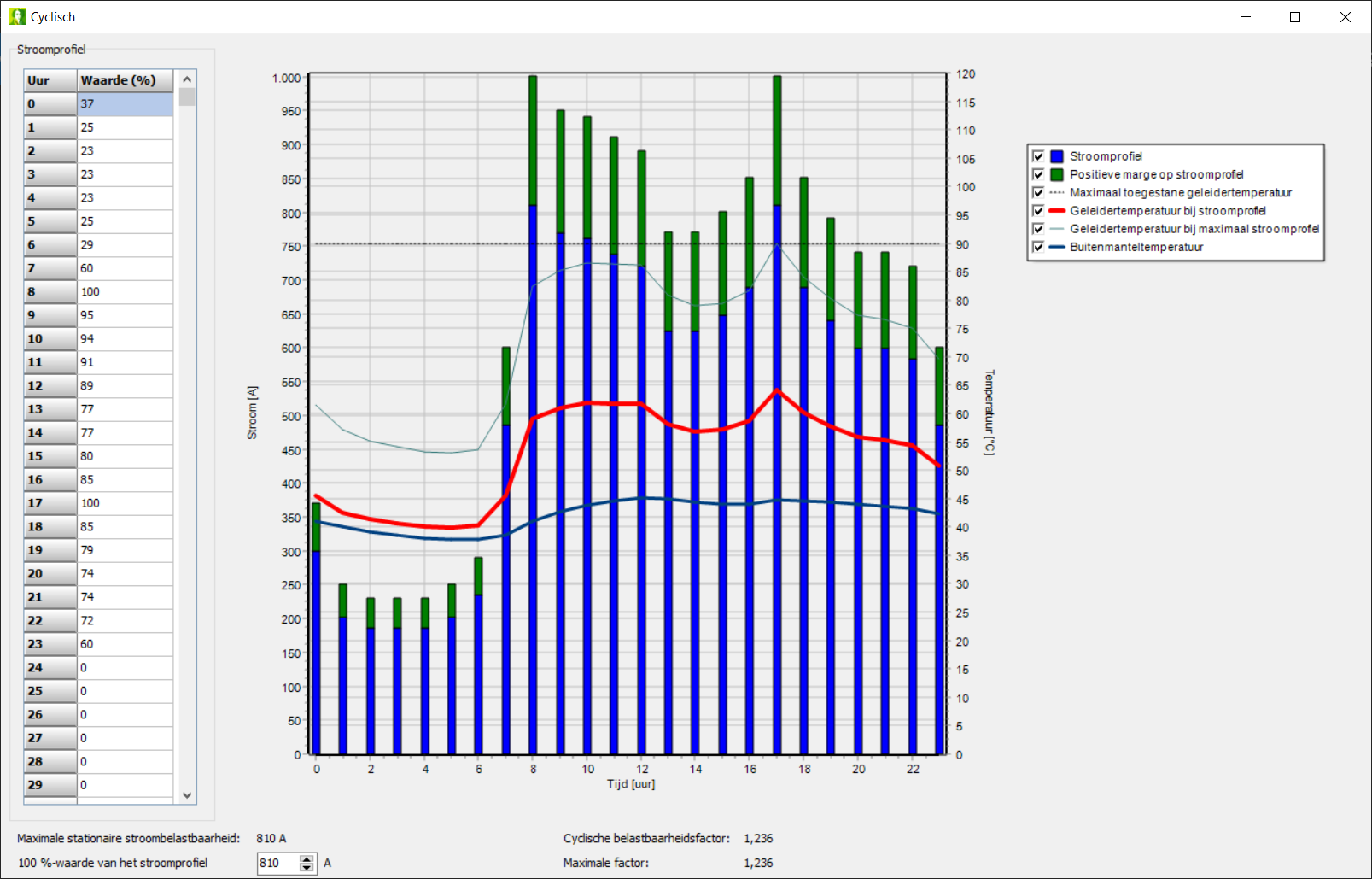
De IEC 60853 standard describes the methods for calculating of de cyclic cable rating and the emergency cable rating.
The dynamic cable rating calculation is based on the fact that a cable, not conducting 100% of the maximum continuous current, has not reached its maximum temperature. Thanks to the dynamic properties of cable and soil, the temperatures respond slowly to a step change in current, enabling the operator to overload the cable during a short time in emergency situations.
Vision Cable Analysis calculates:
These calculations show how much more than the continuous current rating the cables can conduct in case of a cyclic varying load. The cyclic rating depends on the shape of the daily load cycle. These calculations also show how many extra loads can be added to the cable in case of emergencies. The emergency current rating strongly depends on the starting temperature and the emergency duration.
The starting point of Vision Cable Analysis calculations is always the construction of the cable. The program works with all common single- and three-core cables using the known insulation and construction materials.
Each cable type can be inspected in detail and edited in the cable editor. With this cable editor the standard supplied cable database can easily be adapted and expanded.
Vision Cable Analysis can calculate the ampacity for underground and aboveground cables. The program lets you easily adjust the conditions of the cable connections.
For underground cables, depth and position are the most important factors. Nearby heat sources can be added.
Vision Cable Analysis calculates the cable current rating for those cases:
You can download the latest version of Vision Cable Analysis here. Without a license, Vision Cable Analysis can only be used in demonstration mode. For a license or more information, contact info@phasetophase.nl.